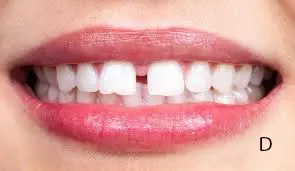
Gap teeth are a space between two teeth, and most commonly the upper front teeth. These are also due to genetics. Gap teeth, also known as daistema. Gap teeth occur in both children and adults and are also the most common feature. The gap can vary widely, depending on the size and location of the space, as well as in temporary spaces.
Introduction
Gap teeth also occur when the jaw line is large, for the size of the teeth gap can also occur. When the jawbone size does not match the teeth size, it also causes a gap. Due to gap teeth, bite issues also occur, and these are not usually harmful, depending on the cause.
- Gum irritations
- Bite issues
- Food getting stuk
- Difficulty chewing efficiently
- tooth cavities
- bone less around the teeth

Causes of gap teeth
Some of the causes are given below:
1. Mismatch of jaw size and tooth size
- If your teeth are small or your jawbone is large, then it causes the extra space between the teeth.
- It is a common genetic trait and is also often passed down through families.
- The teeth will spread out in the resulting form to fill the jaw space if more space is needed.
2. Aging
- New Gap teeth also cause widening over time.
- Your teeth may gradually shift as a result of continuous biting and chewing, as well as minor jaw changes brought about by these changes.
- The front two teeth create space due to slow movement.
- Over the years, teeth become loose and drift apart, creating a new gap, mostly in adults and more aged people.

3. Children’s habits
- Children create pressure in front two teeth and also push them apart.
- In front two teeth space is created when the tongue presses against the front two teeth.
4. Oversized label frenum
- The labial ferum is also an issue that connects the inside of your lips to your gums.
- It can push the front two teeth if too thick or extends too low.
5. Genetics
- If you have a big jaw from one parent and small teeth from another, there may be more space between two teeth.
- Gaps are frequently caused by that additional space, and also most frequently between the front upper teeth.
- Shape variation or tooth gap is frequently inherited.
- A gap may result from some people’s lateral incisors.
6. gum disease
- Gum disease is a chronic infection and the gums and bones that support your teeth.
- Teeth may become loose and move apart, creating a gap, as gum tissues and bone deteriorate.
- Bone loss around the teeth can result from gum inflammation and infections.
- Gums also become red, swollen, and may also bleed when brushing.
7. Missing or unsized teeth
- Misalignments are often caused by neighboring teeth drifting into the space.
- The opposing jaw teeth may also shift into the space, making the spacing worse.
- There are also types of missing teeth:
- Tooth loss from trauma
- tooth extractions
- congenitally missing teeth
Solution for missing teeth
- Dental implant: A Titanium screw also replaces the roots of the missing tooth
- Dental bridge: In a row is good for one or two teeth. A bridge between two healthy teeth for an artificial tooth.
- Partial dentures: It is less stable than an implant or a bridge, and also less expensive, a removable prosthetic fill in multiple gaps.
8. Habits nd behavior
- Pacifier uses beyond age 4: This can push the front teeth forward and also create more space between the front two teeth.
- During swelling or speaking, it can push a part over time, when the tongue presses against the front two teeth.
Treatment
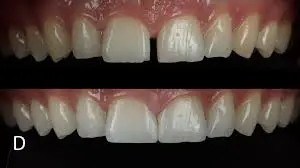
1. Dental bonding
- Moderate or small gaps
- Dental bonding is non-invasive and fast
- For filling the gaps of teeth, a tooth colored resin is applied.
.
2. Vaneeres
- It works; a thin shell of porcelain or composite is bonded to the front of two teeth.
- When teeth are also misshapen or uneven, it causes cosmetic issues.
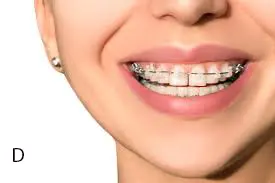
3. Orthodontic treatment
- It is best for gaps caused by a spacing jaw-to-tooth-sized mismatch, or also by habits.
- It also works to move teeth slowly into better alignment.
- After treatment to prevent relapse, often combined with retrainers.
4. Gum disease treatment
- This is caused by periodontal disease.
- Antibiotics, deep cleaning, and possibly surgery to stabilize them before closing the tooth gap.
Non-surgical treatment: “Deep cleaning” scaling and root planing; Their purpose remove tartar plaque and also bacteria from below the gumline. “Antibiotic therapy” has the main purpose is controlling infection and oral antibiotics are used for more aggressive infections.
Surgical treatment: “soft tissue grafts” protect roots, improve appearance, and restore receded gum. “Guided tissue regenerations” have their purpose to rebuild the lost bone to support teeth and also reduce mobility. A procedure is used to place bone material in an area.
Conclusion
Treating the underlying infection must come first when gum disease is caused by gap teeth, before undergoing any cosmetic procedure. Gum disease can result in tooth shifting, bone loss, and gum recession, all of which can lead to a gap. Deep cleaning is typically the first step, which entails using a root planing and scaling technique. Patience may also utilize the technique of braces and other treatments to close any remaining gaps.
FAQs
Q#1 What causes gap teeth?
- Common causes of gap teeth include:
- Gum disease
- Missing teeth
- Unsized teeth
- Genetics
- Habits like tongue thrusting and also thumb suking
Q#2 Are the gap teeth harmful?
- Not at all, they are also simply a cosmetic concern, and however a large gaps can affect:
- Oral hygiene
- speech
- bite alignment
Q#3 Can gap teeth be treated?
Treatment may also include;
- Braces and clear aligners
- Dental bonding
- Crown and bridge
- Frenectomy
Q#4 Is treatment necessary for gap teeth?
No, many people choose to leave it as it is, if the gap is not causing functional problems and also destress. Some people also consider this gap a sign of beauty and good looks.
